Lung cancer is a type of cancer that starts in the lungs and is the leading cause of cancer deaths worldwide. It occurs when abnormal cells grow uncontrollably in one or both lungs, interfering with their normal function. The two main types of lung cancer are non-small cell lung cancer and small cell lung cancer.
Symptoms of lung cancer may vary depending on the stage of cancer and how far it has spread. Early stage symptoms of lung cancer may include cough, chest pain, and shortness of breath, while advanced stage symptoms may include fatigue, weight loss, and bone pain. Some people with lung cancer may not have any symptoms until the cancer has advanced, making early detection and treatment crucial.
In this article, you will learn everything you need to know about lung cancer, including its causes, risk factors, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and prevention. By understanding the basics of lung cancer, you can take steps to reduce your risk of developing the disease, detect it early when it is most treatable, and improve your chances of survival.
Understanding Lung Cancer
Lung cancer is a type of cancer that starts in the lungs and can spread to other parts of the body. It is the leading cause of cancer deaths worldwide. In this section, we will discuss the types, causes, and risk factors associated with lung cancer.
Types of Lung Cancer
There are two main types of lung cancer: non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and small cell lung cancer (SCLC).
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) :
NSCLC is the most common type of lung cancer, accounting for about 85% of all cases. NSCLC can be further divided into three subtypes: adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and large cell carcinoma.
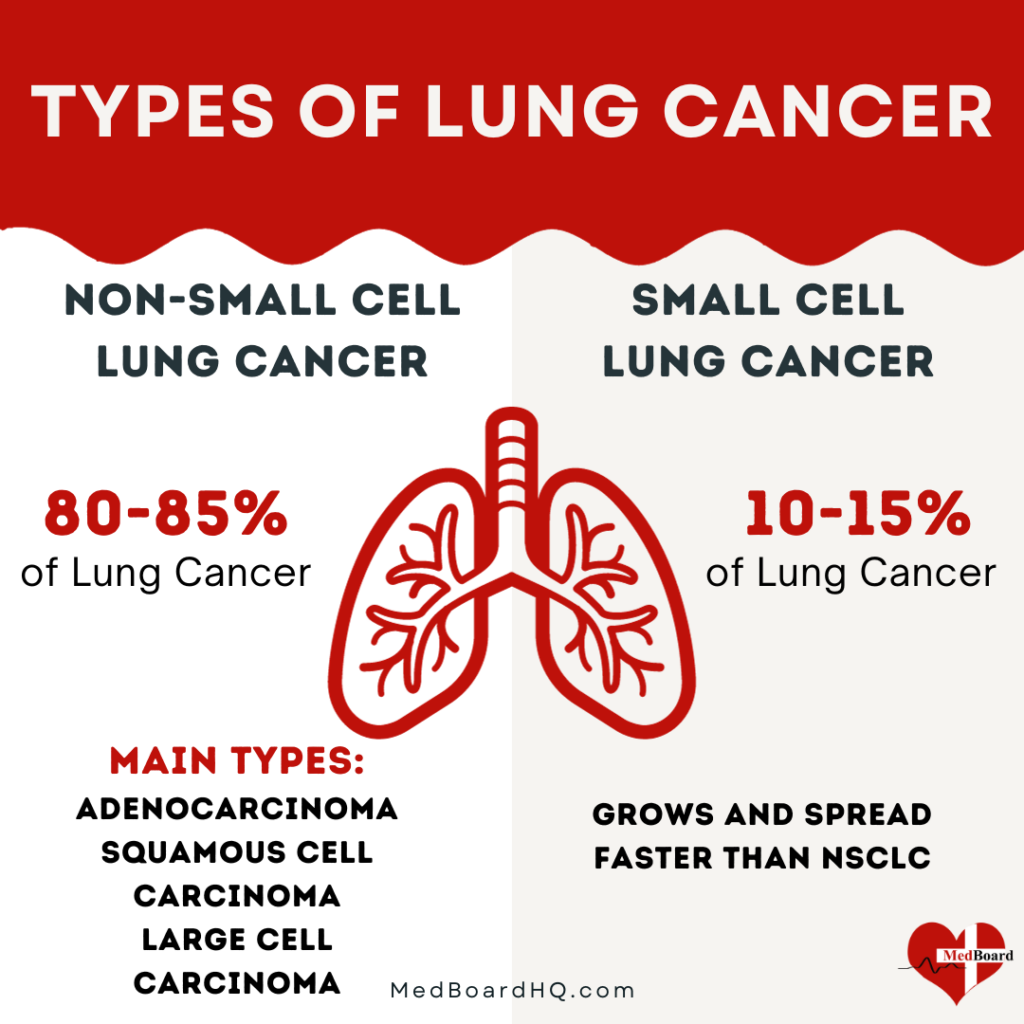
- Adenocarcinoma is the most common subtype and is usually found in the outer parts of the lungs.
- Squamous cell carcinoma is usually found in the central parts of the lungs.
- Large cell carcinoma can occur anywhere in the lungs.
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) :
SCLC is less common, accounting for about 15% of all cases. SCLC is a more aggressive type of lung cancer and is usually found in the central parts of the lungs. It tends to grow and spread quickly, which can make it more difficult to treat.
Causes and Risk Factors
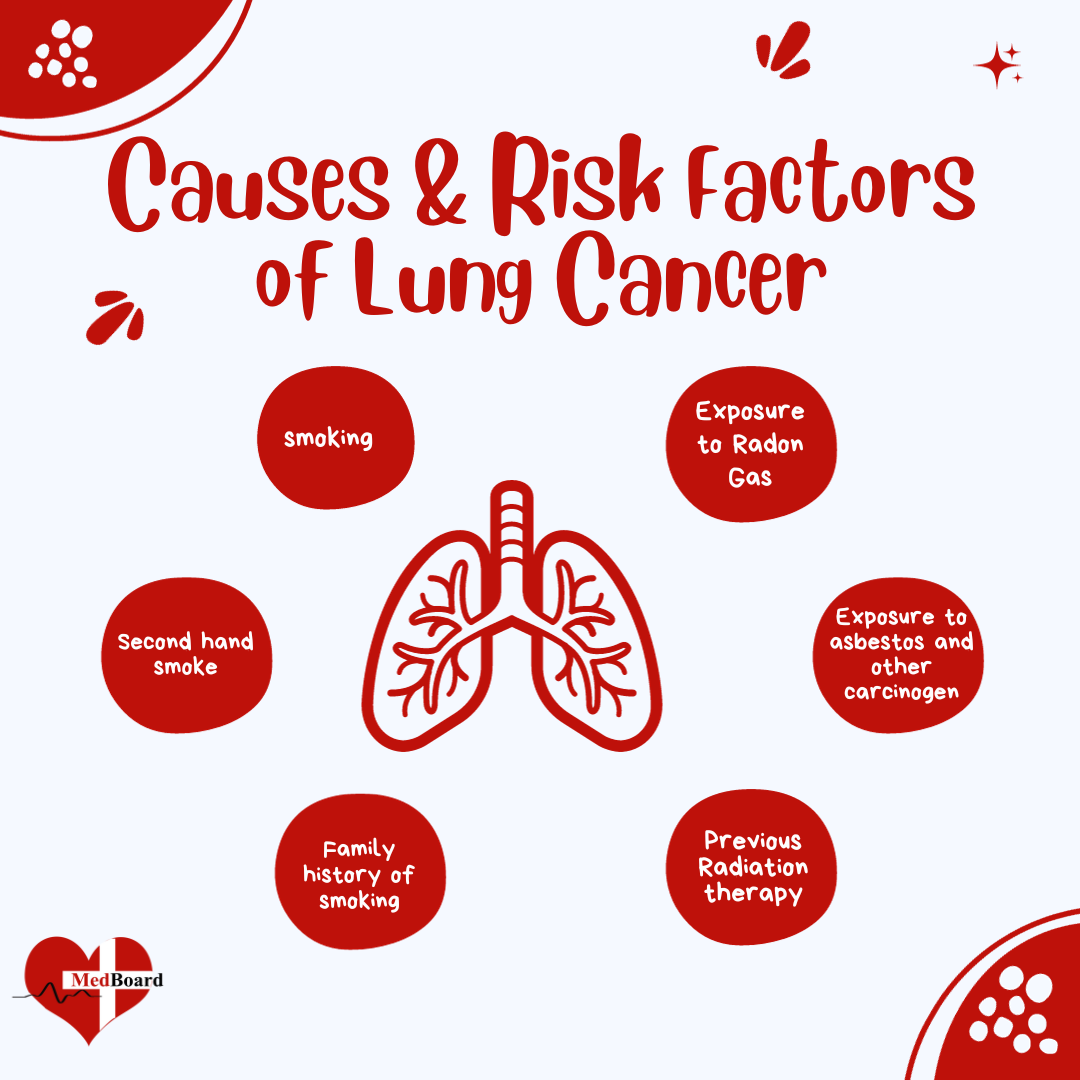
The primary cause of lung cancer is smoking. According to the American Cancer Society, about 80% of lung cancer deaths are caused by smoking. However, not all people who smoke develop lung cancer, and not all people who develop lung cancer have a history of smoking. Other risk factors include:
- Exposure to secondhand smoke
- Exposure to radon gas
- Exposure to asbestos and other carcinogens
- Family history of lung cancer
- Previous radiation therapy to the chest
It is important to note that anyone can develop lung cancer, regardless of their age, gender, or ethnicity. However, certain groups of people may be at a higher risk, such as those who smoke or have a family history of lung cancer.
In conclusion, understanding the types, causes, and risk factors associated with lung cancer is crucial for early detection and timely medical intervention. If you are at a higher risk for lung cancer, it is important to talk to your doctor about screening options and ways to reduce your risk.
Symptoms and Signs of Lung Cancer
Lung cancer is a serious disease that can often go undetected until it has reached an advanced stage. Therefore, it is important to be aware of the symptoms and signs of lung cancer so that it can be detected early and treated more effectively.
The most common symptoms of lung cancer include:
- A persistent cough that does not go away or gets worse
- Coughing up blood or rust-colored sputum (spit or phlegm)
- Chest pain that worsens with deep breathing, coughing, or laughing
- Hoarseness
- Loss of appetite
- Unexplained weight loss
- Shortness of breath
- Feeling tired or weak
- Bone pain
- Headache
It is important to note that these symptoms can also be caused by other conditions, such as a respiratory infection or asthma. However, if these symptoms persist for more than a few weeks, it is important to see a doctor.
In addition to the above symptoms, there are some less common symptoms of lung cancer, including:
- Swelling in the face or neck
- Difficulty swallowing
- Changes in the shape or size of the fingers and nails, known as “clubbing”
- A new onset of wheezing
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to see a doctor as soon as possible. Early detection of lung cancer can greatly improve the chances of successful treatment.
It is also important to note that some people with lung cancer may not experience any symptoms at all. This is why regular screenings are recommended for people who are at high risk for lung cancer, such as smokers or those with a family history of the disease.
Diagnosis of Lung Cancer
When it comes to diagnosing lung cancer, there are several tests that doctors may use to confirm the presence of cancerous cells. These tests can include imaging tests, biopsy, and lab tests.
Imaging Tests

Imaging tests are often the first step in diagnosing lung cancer. These tests use various technologies to create images of the lungs, which can help doctors identify any abnormalities. Some common imaging tests that may be used to diagnose lung cancer include:
- X-ray: An X-ray uses radiation to create images of the lungs.
- CT scan: A CT scan uses X-rays and computer technology to create detailed images of the lungs.
- MRI: An MRI uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create detailed images of the lungs.
- PET scan: A PET scan uses a special dye that is injected into the body to create images of the lungs.
Biopsy and Lab Tests
If imaging tests reveal abnormalities in the lungs, doctors may perform a biopsy to confirm the presence of cancerous cells. During a biopsy, a small sample of tissue is removed from the lung and examined under a microscope for signs of cancer.

There are several different types of biopsies that may be used to diagnose lung cancer, including:
- Bronchoscopy: A bronchoscopy uses a thin, flexible tube with a camera on the end to examine the airways and collect tissue samples.
- Needle biopsy: A needle biopsy uses a long, thin needle to collect tissue samples from the lung.
- Surgery: In some cases, doctors may need to perform surgery to remove a larger sample of tissue from the lung.
Lab tests may also be used to diagnose lung cancer. These tests can help doctors identify specific types of cancer and determine the best course of treatment. Some common lab tests that may be used to diagnose lung cancer include:
- Blood tests: Blood tests can help doctors identify certain proteins or markers that may be present in the blood of people with lung cancer.
- Molecular testing: Molecular testing can help doctors identify specific genetic mutations that may be present in lung cancer cells.
- Pathology testing: Pathology testing involves examining tissue samples under a microscope to identify the type of cancer and determine how advanced it is.
Overall, diagnosing lung cancer can be a complex process that involves several different tests and procedures. However, with early detection and treatment, many people with lung cancer are able to achieve positive outcomes.
Stages of Lung Cancer
Lung cancer is staged according to the size of the tumor and how far it has spread. Knowing the stage of lung cancer is important because it helps doctors determine the best treatment plan.
There are two main types of lung cancer: Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) and Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC). The stages of NSCLC are different from the stages of SCLC.
Stages of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC)
NSCLC is divided into four stages:
- Stage 1: The cancer is only in the lung and has not spread to the lymph nodes or other parts of the body.
- Stage 2: The cancer has spread to the lymph nodes near the lung.
- Stage 3: The cancer has spread to the lymph nodes in the middle of the chest or to other nearby organs.
- Stage 4: The cancer has spread to other parts of the body, such as the liver, bones, or brain.
Stages of Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC)
SCLC is divided into two stages:
- Limited Stage: The cancer is only in one lung and nearby lymph nodes.
- Extensive Stage: The cancer has spread to other parts of the body.
It’s important to note that the stages of lung cancer can vary depending on the type of cancer and the individual case. Talk to a doctor for more information about the specific stage of lung cancer and the best treatment options.
Treatment Options for Lung Cancer
There are several treatment options available for lung cancer, and the choice of treatment depends on several factors such as the type and stage of cancer and the patient’s overall health. In this section, we will discuss the most common treatment options for lung cancer.
Surgery
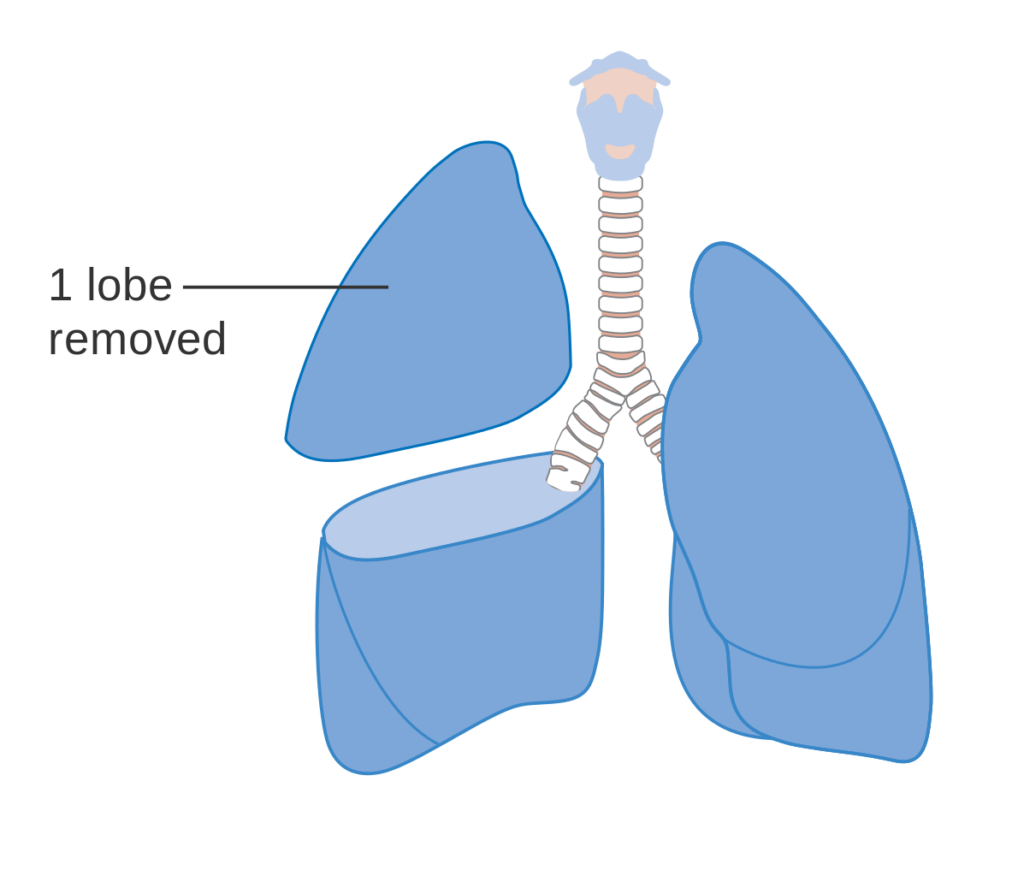
Surgery is often the first line of treatment for early-stage lung cancer. The goal of surgery is to remove the cancerous tissue from the lung. The type of surgery depends on the size and location of the tumor. The most common types of surgery for lung cancer are:
- Lobectomy: Removal of the entire lobe of the lung.
- Pneumonectomy: Removal of the entire lung.
- Segmentectomy or wedge resection: Removal of a small section of the lung.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy uses high-energy radiation to kill cancer cells. It can be used alone or in combination with other treatments. The radiation can be delivered externally or internally. External radiation therapy is delivered from a machine outside the body, while internal radiation therapy is delivered through a radioactive source placed inside the body.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells. It can be used alone or in combination with other treatments. Chemotherapy drugs are usually given intravenously, but they can also be taken orally. Chemotherapy is often used to treat advanced-stage lung cancer.
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy is a type of treatment that helps the immune system to fight cancer. It works by blocking the proteins that allow cancer cells to hide from the immune system. Immunotherapy drugs are usually given intravenously. Immunotherapy is often used to treat advanced-stage lung cancer.
In summary, there are several treatment options available for lung cancer, including surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy. The choice of treatment depends on several factors and should be made in consultation with a healthcare professional.
Living with Lung Cancer
Being diagnosed with lung cancer can be a life-changing experience. While treatment is important, managing the side effects, psychological impact, and finding support and resources are also crucial to living with lung cancer.
Managing Side Effects
Lung cancer treatment can cause a range of side effects, including fatigue, nausea, and pain. Patients should work closely with their healthcare team to manage these side effects. This may include medication, lifestyle changes, or complementary therapies such as acupuncture or massage.
It is also important for patients to maintain a healthy diet and exercise routine. This can help reduce side effects and improve overall well-being. Patients should discuss any exercise plans with their healthcare team before starting.
Psychological Impact
A lung cancer diagnosis can also have a significant psychological impact. Patients may experience anxiety, depression, or fear. It is important for patients to seek support from family, friends, or a mental health professional.
Support groups can also be helpful for patients to connect with others who are going through similar experiences. Many cancer centers offer support groups for patients and their families.
Support and Resources
Finding support and resources is important for patients with lung cancer. Patients and their families should work with their healthcare team to identify resources in their community. This may include financial assistance, transportation, or home care services.
The American Lung Association and the Lung Cancer Research Foundation are also resources for patients and their families. These organizations offer information about lung cancer, support groups, and advocacy efforts.
Living with lung cancer can be challenging, but with the right support and resources, patients can improve their quality of life.
Prevention and Early Detection of Lung Cancer
Prevention and early detection are crucial in the fight against lung cancer. Here are some steps that can be taken to reduce the risk of developing lung cancer:
- Stop smoking: Smoking is the leading cause of lung cancer, accounting for 85% of all cases. Quitting smoking is the most effective way to reduce the risk of lung cancer. Even if someone has smoked for many years, quitting can still reduce their risk of developing lung cancer.
- Avoid secondhand smoke: Secondhand smoke is also a risk factor for lung cancer. People who are regularly exposed to secondhand smoke should take steps to reduce their exposure.
- Test for radon: Radon is a radioactive gas that is found in soil and rocks. It can seep into homes and buildings and increase the risk of lung cancer. Testing for radon and taking steps to reduce exposure can help prevent lung cancer.
- Reduce exposure to carcinogens: Exposure to certain chemicals and substances, such as asbestos and diesel exhaust, can increase the risk of lung cancer. Taking steps to reduce exposure to these substances can help prevent lung cancer.
Early detection is also important in the fight against lung cancer. When lung cancer is detected at an early stage, it is more treatable and the chances of survival are higher. Here are some ways that lung cancer can be detected early:
- Screening: Screening tests, such as low-dose CT scans, can help detect lung cancer in people who are at high risk for the disease. Talk to a healthcare professional about whether screening is appropriate.
- Know the symptoms: Knowing the symptoms of lung cancer can help with early detection. Symptoms may include coughing, chest pain, shortness of breath, and unexplained weight loss. If someone experiences any of these symptoms, they should talk to a healthcare professional.
Prevention and early detection are key in the fight against lung cancer. By taking steps to reduce the risk of developing lung cancer and knowing the signs and symptoms of the disease, people can increase their chances of survival.
Latest Research and Developments in Lung Cancer
Lung cancer is one of the most common types of cancer worldwide, and research into its prevention, early detection, and treatment is ongoing. Here are some of the latest research and developments in lung cancer:
Prevention
Tobacco is the leading cause of lung cancer, and smoking cessation is the most effective way to prevent the disease. However, there are other ways to reduce the risk of developing lung cancer, such as:
- Avoiding exposure to secondhand smoke
- Reducing exposure to radon, a radioactive gas that is the second leading cause of lung cancer
- Limiting exposure to air pollution and occupational carcinogens
Early Detection
Early detection of lung cancer can improve the chances of successful treatment. Currently, the most common method of early detection is low-dose computed tomography (LDCT) screening for high-risk individuals. However, research is ongoing to develop new methods of early detection, such as blood tests and breath analysis.
Treatment
Treatment for lung cancer depends on the stage of the disease and other factors, such as the patient’s overall health. The main treatments for lung cancer are surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. However, there are also newer treatments available, such as targeted therapy and immunotherapy.
Targeted therapy involves using drugs that target specific molecules in cancer cells, while immunotherapy involves using drugs that help the immune system fight cancer. These treatments have shown promise in clinical trials and are being used to treat some patients with advanced lung cancer.
Research
Research into lung cancer is ongoing, and there are many clinical trials investigating new treatments and diagnostic methods. The National Cancer Institute (NCI) is one of the leading organizations funding research into lung cancer, and it has several ongoing initiatives, such as the Lung Cancer Screening Trial and the Lung Cancer Mutation Consortium.
In addition to clinical trials, there is also research being done on the genetics of lung cancer. Recent studies have identified several genetic mutations that are associated with an increased risk of developing lung cancer, and this knowledge could lead to new targeted therapies in the future.
Overall, the latest research and developments in lung cancer are providing hope for better prevention, early detection, and treatment of this deadly disease. However, more research is needed to fully understand the biology of lung cancer and develop more effective treatments.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the different types of lung cancer?
There are two main types of lung cancer: non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and small cell lung cancer (SCLC). NSCLC is the most common type of lung cancer, accounting for about 85% of cases. SCLC is less common, accounting for about 10-15% of cases.
What are the causes of lung cancer in women?
The causes of lung cancer in women are similar to those in men. The most common cause of lung cancer is smoking, which is responsible for about 85% of lung cancer cases. Other risk factors include exposure to secondhand smoke, air pollution, radon gas, and occupational exposure to certain chemicals.
What are the stages of lung cancer?
There are four stages of lung cancer, ranging from Stage I (early stage) to Stage IV (advanced stage). The stage of lung cancer is determined by the size and location of the tumor, as well as whether the cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes or other parts of the body.
What is the survival rate for lung cancer?
The survival rate for lung cancer varies depending on the stage of the cancer at the time of diagnosis. According to the American Cancer Society, the 5-year survival rate for people with Stage I NSCLC is about 56%, while the 5-year survival rate for people with Stage IV NSCLC is about 5%. The 5-year survival rate for people with SCLC is about 6%.
How does lung cancer affect the body?
Lung cancer can affect the body in a number of ways. Common symptoms of lung cancer include coughing, chest pain, shortness of breath, fatigue, and unexplained weight loss. Lung cancer can also cause complications such as pneumonia, fluid buildup in the chest, and a collapsed lung.
What are some interesting facts about lung cancer?
- Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer deaths worldwide.
- Smoking is responsible for about 85% of lung cancer cases.
- Lung cancer is more common in older adults, with the average age of diagnosis being 70 years old.
- Women who smoke are more likely to develop lung cancer than men who smoke.
- Lung cancer can be treated with surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy.




